Add SSO with Microsoft Entra using SAML 2.0
Requirements: Cloud SSO
Introduction
The Security Assertion Markup Language 2.0 (or SAML 2.0) is a flexible protocol that was designed to cover a wide variety of scenarios called "profiles". A common profile called Web SSO defines a standardized way for applications to add Single Sign-on (SSO) support to their applications. SSO-enabled applications (also known as Service Providers) delegate authentication to authentication servers (also known as Identity Providers). For example, Microsoft Entra is a widely used Identity Provider that allows users to log in to supported applications using the Microsoft Enterprise accounts assigned to them by their organization.
Because SAML 2.0 is flexible in what it offers, it is often complex to configure and implement. The SAMLWeb and SAMLDesktop components from Cloud SSO simplifies the implementation with an easy-to-use interface. The components handles interpreting metadata documents, building authentication and logout requests, and parsing and validating responses.
Before getting started, a few terms should be defined:
- Identity Provider—A server that issues SAML assertions about an authenticated subject.
- Service Provider—An application that relies on an Identity Provider for authentication.
- Subject—An entity (typically a user) that will be authenticated by the Identity Provider for a Service Provider.
- Assertion—An XML message that contains security information and details about a subject.
- Protocol Binding—A description of the communication protocols (i.e., HTTP-Redirect or HTTP-POST) being used by the Identity Provider and Service Provider.
In the following guide, we will set up Microsoft Entra as the Identity Provider for your application, which will use the SAMLWeb component to act as a Service Provider. Though we mainly focus on the SAMLWeb component, the SAMLDesktop component is very similar. See desktop considersations for options during the setup and the example at the end of the article for the SAMLDesktop component.
Contents
- How SAML Works
- Creating a New SAML Application
- Authenticating a User with the SAMLWeb component
- Additional Notes
- SAMLDesktop Example
How SAML Works
SAML 2.0 typically follows the same flow for Web SSO. Before starting, the Service Provider configures the Identity Provider with knowledge about how to communicate with it and vice versa. Then a user of the Service Provider requests to be authenticated. The Service Provider will build an authentication request and communicate it to the Identity Provider's SingleSignOnService URL using the specified protocol binding. Typically, HTTP-POST and HTTP-Redirect are both supported by Identity Providers.
Next, the Identity Provider will go through the process of authenticating the current user. This step may be skipped if the user already has an authentication session with the Identity Provider. Once the user has been authenticated, the Identity Provider will issue an assertion using the authenticated user as the subject. Depending on the Identity Provider, it will then XML sign the assertion, the SAML response, or both before sending the SAML response back to the Service Provider to the specified AssertionConsumerService URL. The URL will also specify a protocol binding that does not need to match the protocol binding used by the SingleSignOnService. Typically, because of the size of the response, HTTP-POST is used.
The AssertionConsumerService (ACS) URL will receive the HTTP request and parse the SAMLResponse parameter from it. It will then validate and parse the SAML response and its accompanying assertion. If everything checks out, the Service Provider can then allow the current user to be logged in.
Creating a New SAML Application
To register your application as a Service Provider so that it can use Microsoft Entra ID as the Identity Provider, we will need to use the Microsoft Azure Portal. The first step from within the portal is to navigate to the "Enterprise applications" service. On this page, you will see all the applications that have been registered with your Microsoft organization. To start the process, select "New application" to be brought to the Microsoft Entra Gallery. On this page, many services have already been configured, but because we are creating a new web application, you will want to select "Create your own application". This will prompt the Azure Portal to ask you the name of your application and what you are looking to do with your application. For a new application that supports SAML, we will want to select "Intergrate any other application you don't find in the gallery (Non-gallery)".
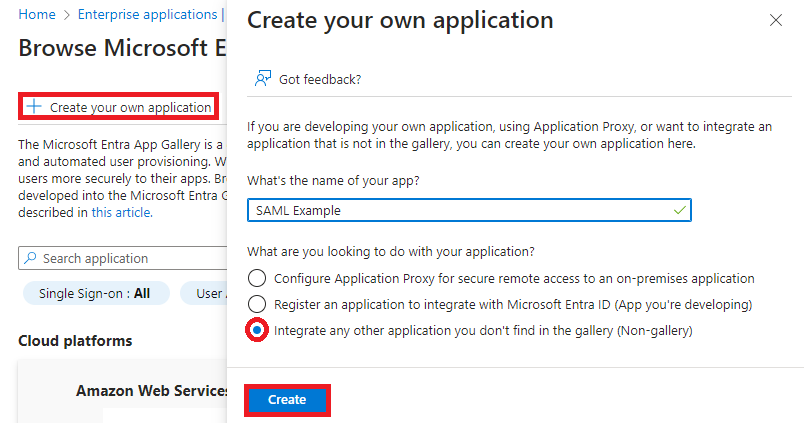
After some time, the new application will be initialized. Within the application, select the "Single sign-on" section to begin configuring the application for SSO using SAML. Because we are using SAML, we will want to select SAML, which will bring us to the configuration page for our application.
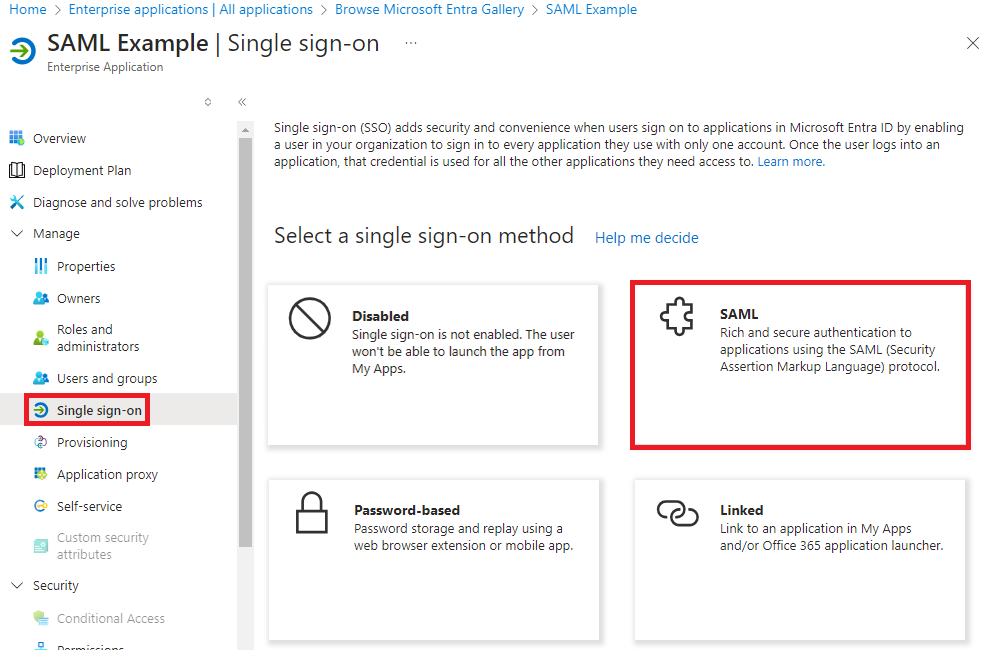
To start, select "edit" in the "Basic SAML Configuration" section.
Basic SAML Configuration
The first step in configuring your application as a Service Provider is configuring how Microsoft Entra will recognize the application and where it should send SAML responses to. Microsoft Entra supports uploading a SAML metadata document that describes your Service Provider, but we will be manually configuring the Service Provider in this guide.
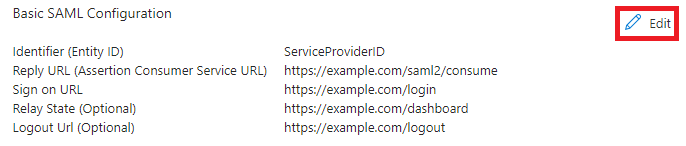
Entity Id
The "Entity Id" or "Identifier" is a required field. It is the unique Id for the Service Provider (our application) and should be a unique value within the organization. The Entity Id will be set to "ServiceProviderId" in the following example.
Assertion Consumer Service
The "Assertion Consumer Service URL" or "Reply URL" is also a required field. It defines the location within your web application that will handle the authentication responses from Microsoft Entra ID. This location will receive a SAML response through the HTTP-POST or HTTP-Redirect bindings (more on that later). In the next example, we have set this to "https://example.com/saml2/consume", which is where we will be processing the SAML response in the following sections. See Desktop Consideration for more information about ACS URLs for desktop applications.
Sign on URL
The Sign on URL is an optional field. When the application is assigned to a user, it will be available to the user through the "My Apps" page. When the application is selected, the user will be directed to the URL defined here. Typically, this will be the login page for the application. In the following example, we will set this to "https://example.com/login", which will start the SAML authentication process for our user.
Relay State
The Relay State is an optional field. When this value is set, Microsoft Entra will set the RelayState to the specified value if it was not set in the authentication request. The RelayState is typically used by the Service Provider to keep track of where a user was in the application when they requested to be authenticated. This is often useful in applications in which certain sections of the application are accessible to everyone. If someone has navigated through a website, when they log in, they typically expect to be put back at the location where they started the request. If the RelayState is not set, this will then be the default location to place users at when they login. The following example uses "https://example.com/dashboard" as the default Relay State.
Logout URL
The Logout URL is an optional field. Because Microsoft supports Single Logout (SLO), this URL will be the location a user is returned to after making a SAML logout request. In the following example, we will set this to "https://example.com/logout", which will finish the logout process for our user. See Desktop Consideration for more information about logout URLs for desktop applications.
Optional Settings
With the basic SAML configuration settings configured, the next step is to configure some optional settings depending on the requirements for your application. The following sections, "Attributes & Claims" and "SAML Certificates", may not be required but may be useful depending on your application's requirements.
Attributes and Claims
This section is provided to give control over how Microsoft builds the assertion that is consumed by the application. When editing this page, the first (and required) claim is the user's Unique User Identifier (UPN) as the Name Id for the assertion. The Name Id is used in an assertion to describe who is being described by the assertion.
Along with the Name Id, other claims like email address, first name, and last name come preconfigured. If additional user or group claims should be added to the assertion, they can be added through this page.
SAML Certificates
There are two subsections that can be configured in this section. The first describes how and when the Identity Provider will sign the responses they issue. By default, Microsoft Entra will sign only the assertion using SHA-256. Through this page, you can select to sign just the SAML response or both the SAML response and assertion. For our purposes, we will have Microsoft Entra sign both. Additionally, you can opt to use SHA-1, but we will leave it set to use SHA-256. Also on this page, you can set an email that will be notified when the certificate that is used to sign the requests will expire. We will have this set to "admin@example.com".
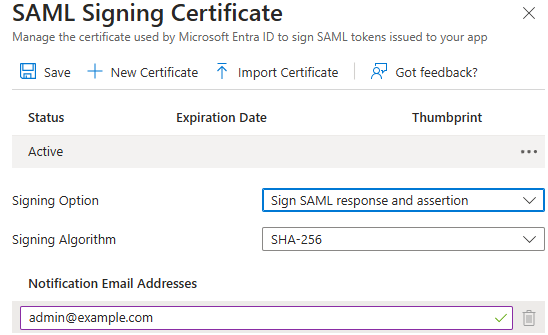
The next subsection describes how your Service Provider will sign requests. This is an optional feature but is recommended if your application is looking to have SLO supported. For our purposes, we will not be configuring this section. To configure this section, first select "Require verification certificates" and then upload the public certificate (saved in a .cer file) to the portal.
Desktop Considerations
When setting up the SAML application to be used with the SAMLDesktop component, it is typical to use a localhost URL rather than a hosted domain. This is due to the SAMLDesktop component hosting an embedded web server for your desktop application. Also, to avoid issues with SSL/TLS, HTTP is typically preferred over HTTPs. If HTTPS is required, then the SAMLDesktop component can enabled SSL/TLS for its embedded webserver. Additionally, the localhost URL that is configured must specifiy a port number. For example "http://localhost:8080" would be a valid localhost URL. However, the port specified in the registration does not need to match the port used by the component.
Additionally, since the embedded web server is not running all the time, the SAMLDesktop component does not support or handle logout requests. If required, using the SAMLWeb component on a hosted web server might be a better option.
Metadata Information
Microsoft allows you to either download the metadata document or make a request to a URL to retrieve it. For our example, we will want to save the URL to make a request to Microsoft Entra to retrieve it. You can copy the URL from the location marked in the "SAML Certificates" section.
With the metadata information, you are now ready to configure the SAMLWeb (or SAMLDesktop) component within your web application to enable it as a Service Provider for your user.
Authenticating a User with the SAMLWeb component
The following examples assume that the accompanying information is True about the application. First, the domain for the web application is "example.com" and the webserver supports HTTPS. Next, the application will be making requests using the HTTP-Redirect binding but receiving responses using the HTTP-Post binding. Finally, the web server has a specific location for handling responses that is separate from the locations that a user interacts with. In the previous section, the following information was configured.
- ACS URL – https://example.com/saml2/consume
- Entity Id – ServiceProviderId
- Metadata URL - https://login.microsoftonline.com/11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555/federationmetadata/2007-06/federationmetadata.xml?appid=66666666-7777-8888-9999-000000000000
- Name Id – User's Email
Additionally, we have requested that both the SAMLResponse and Assertion elements be signed when the Identity Provider issues the assertion. Finally, we will request the metadata document rather than downloading it.
Configure Metadata
Before building a SAML request or processing a SAML response, the component will need to be configured with information about the Service Provider and Identity Provider. The following will always need to happen.
First, the Identity Provider's information needs to be requested, or if already cached, loaded into the component. To request the metadata document, use the RequestIdentityMetadata method, which accepts a URI. If the Identity Provider's metadata is already cached or downloaded, the LoadIdentityMetadata method can be used to load the metadata either from a file or directly through a string. Once either method is finished, the IdentityProviderMetadata, IdentityProviderSigningCert, and IdentityProviderURIs properties are populated. Because Microsoft offers the metadata through a requestable endpoint, we will use the RequestIdentityMetadata method instead of the LoadIdentityMetadata method.
saml.RequestIdentityMetadata("https://login.microsoftonline.com/11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555/federationmetadata/2007-06/federationmetadata.xml?appid=66666666-7777-8888-9999-000000000000");
Next, the component needs to know the AssertionConsumerService URI being used by the application. If the application uses multiple endpoints, each one can be loaded into the ServiceProviderURIs collection. Microsoft supports having multiple ACS endpoints using the HTTP-POST binding. For our application, however, we will be using only a single URI.
URI acs = new URI();
acs.URIType = SAMLURITypes.sutACS;
acs.Location = "https://example.com/saml2/consume ";
acs.BindingType = subPost;
saml.ServiceProviderURIs.Add(acs);
With these two steps, we are now ready to build a SAML request for authenticating a user.
Build a SAML Request
Along with the setup steps, we will need to configure the component to know how we want our request formatted. Because we are looking to make a simple authentication request, we will be configuring only the RelayState property and the Issuer and Binding fields from the SAMLRequestSettings property. Once the SAML request has been configured, the BuildAuthnRequest method will create the request. Along with configuring the component to build the SAML request, you will need to save the Id and Issuer fields for validation later.
Relay State
The RelayState parameter is similar to the State parameter if you are familiar with OAuth or OpenID Connect. If an Identity Provider is provided with the RelayState parameter during a SAML request, it will return the exact value in its response. For example, if the Service Provider sets the RelayState to "value1", then along with the SAMLResponse parameter, the Identity Provider would also set the RelayState parameter to "value1". As a note, the RelayState parameter is separate from the SAMLResponse parameter and is not found within the SAML response.
A real-world example of how the RelayState parameter could be used is to keep track of where a user is in the application when they request to be authenticated. This allows your application to return the user to their previous location so they have a smoother experience. For our example, we will be setting the RelayState parameter to "https://example.com/dashboard" so that our application can return the user to the dashboard of our application.
Issuer
The Issuer field in the SAMLRequestSettings property needs to be set to the Entity Id that was configured during the setup phase. This configures the component to issue the SAML request in the name of your registered Service Provider. In our example, this will be set to "ServiceProviderID".
Request Binding
The Binding field in the SAMLRequestSettings property defines the binding that will be used by the application to make the request. Depending on how this field is set, the component will change how the SAML request is built. Typically, the HTTP-Redirect binding is used which is what we will be using in our example. When configured this way, only the SAMLRequestURL property will be set.
SAML Request Example
This example shows how to build a SAML request using the HTTP-Redirect binding that will be for Microsoft Entra ID, who is acting as the Identity Provider. The example saves the SAML request's Id to a safe location for later.
//Setup Request
saml.SAMLRequestSettings.Issuer = "ServiceProviderID";
saml.SAMLRequestSettings.Binding = SAMLBindings.sbHTTPRedirect;
saml.RelayState = "https://example.com/dashboard";
//Build Request and Save Request ID
saml.BuildAuthnRequest();
string requestId = saml.SAMLRequestSettings.Id;
//Redirect the User
Redirect(saml.SAMLRequestURL);
Parse and Validate a SAML Response
After the user has authenticated with the Identity Provider as a result of the SAML request being made, the user will be redirected back to your application. The location of this redirect is defined by the ACS URI that is configured during the metadata phase. Because the example uses the HTTP-POST binding for the ACS URI, the response will have two parameters. The first will be the SAMLResponse parameter, and the second will be the RelayState parameter. The SAML component will then process the SAML response by parsing and validating the SAMLResponse parameter and its assertion.
The component will need to be configured with the same setup settings (Identity Provider's Metadata and Service Provider's URIs) for validation and verification reasons. Additionally, the Id and Issuer fields in the SAMLRequestSettings property will need to be configured as they are also needed to validate SAML responses.
Providing the SAMLResponse to the Component
The SAML component offers three different ways to provide the SAMLResponse parameter to the component. First, if the component is being used in an ASP.NET or Java Spring project, the component can get the SAMLResponse directly from the environment. For ASP.NET, this is the HTTPContext, and for Java Spring this is from the HttpServletRequest. If using ASP.NET core, this HTTPContext will need to be provided in the constructor when creating the SAML object.
If the component is being used in a different web project, then it will need to be provided with the necessary information. If the project provides the raw HTTP headers and body, the SAMLResponseHeaders and SAMLResponseBody properties can be set with those values. As a note, the SAMLResponseHeaders need to contain both the HTTP request line and the HTTP headers for the component to be able to properly parse the information needed.
If the project provides the parsed values, set the ResponseContent field from the SAMLResponseInfo property with the parsed SAMLResponse parameter. The SAMLResponse parameter can be left in Base64 encoding but needs to be URL-decoded before providing it to the component.
Configure SAMLRequestSettings
The Id and Issuer fields in the SAMLRequestSettings property need to be configured so the SAML component can validate the SAMLResponse parameter and its assertion correctly. The Id field is used to validate the InResponseTo attribute, which is used to ensure that the SAML response being validated is "in response to" a request made by this application.
The Issuer field is used to validate the Audience element found within the assertion. The Audience element describes who the assertion is meant to be used by. It is important to trust only those assertions that were meant for the Service Provider and not for some other Service Provider.
In some projects, it is not a simple task to know these values beforehand. In these cases, the SAMLResponse and Assertion events will fire with the values that were parsed from the SAML response. You can then use the values to check if they exist in your system and set the fields accordingly if they are present.
SAMLResponse Example
In this example, we will provide the HTTPContext to the SAML constructor before loading in the Identity Provider's metadata information and the Service Provider's ACS URI. This way, the SAML component will parse the SAMLResponse parameter directly from the HTTPContext. It will then configure the Issuer and Id fields in the SAMLRequestSettings property before calling ProcessSAMLResponse.
//Create new SAML Object, passing in the HttpContext
SAMLWeb saml = new SAMLWeb(HttpContext);
//Load Identity Provider's Metadata
saml.RequestIdentityMetadata("https://login.microsoftonline.com/11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555/federationmetadata/2007-06/federationmetadata.xml?appid=66666666-7777-8888-9999-000000000000");
//Configure Service Provider's ACS URI
URI acs = new URI();
acs.URIType = SAMLURITypes.sutACS;
acs.Location = "https://example.com/saml2/consume ";
acs.BindingType = subPost;
saml.ServiceProviderURIs.Add(acs);
//Configure saved information about the SAML request.
saml.SAMLRequestSettings.Issuer = "ServiceProviderID";
saml.SAMLRequestSettings.Id = requestId;
//Process the SAML response.
saml.ProcessSAMLResponse();
Additional Notes
Process versus Parse
Typically, the ProcessSAMLResponse method is all that is needed to parse and validate a SAML response. If special circumstances are required, then the Parse* and Validate* methods can be used to manually go through each step that the ProcessSAMLResponse method would normally handle. The following methods would be equivalent to the ProcessSAMLResponse method.
- ParseSAMLResponse
- ValidateSAMLResponse
- ParseAssertion
- ValdiateAssertion
An important note when using these separated methods is that the Parse* methods must be called before the Validate* methods so that the component has the information needed to validate the SAMLResponse or assertion. For this reason, if the SAMLResponse or assertion has not already been validated, the information from the Parse* methods should be trusted only after the methods have been called.
Validation Process
When the SAML component validates a SAML response or assertion, it will follow the same steps whether the ProcessSAMLResponse method is used or the ValidateSAMLResponse and ValidateAssertion methods are used. In certain situations, your application may want to skip certain checks. The SAMLResponseValidationFlags and AssertionValidationFlags configuration settings can be configured to control which checks are skipped by the SAML component when validating.
When validating a SAML response, the following elements or attributes are verified and validated:
- Signature
- Issuer
- InResponseTo
- Destination
- Status
When validating an assertion, the SAML component has to check more attributes and elements than when it checks the SAML response. The following sections (each with multiple checks) are verified and validated in an assertion:
- Signature
- Issuer
- Conditions
- Subject
- AuthnStatement
Signature
Although optional for both a SAML response and assertion, typically at least one (if not both) is signed by the Identity Provider. These signatures are verified to ensure that a third party has not tampered with the response. To verify a signature, the IdentityProviderSigningCert property needs to be set. Typically, this is populated through the RequestIdentityMetadata or LoadIdentityMetadata methods.
Issuer
The Issuer element is required to be present in the SAMLResponse and the Assertion elements. This element allows the SAML component to ensure that the Identity Provider that has been configured is the one that issued the SAML response and assertion. To validate this, the component requires that the EntityId field is set in the IdentityProviderMetadata property.
Conditions
The Conditions element is found only in an assertion. They describe various conditions that need to be met for the assertion to be considered valid. First, the NotBefore and NotOnOrAfter attributes are checked to ensure that the assertion is still in a valid time period. If it is expired, a new assertion should be requested.
Next, the AudienceRestriction element is checked, which is within the Conditions element. An AudienceRestiction element is made up of one or more Audience elements. An Audience element allows the Identity Provider to describe who the assertion was intended for. This Audience element must match the Entity Id ("ServiceProviderId") of your configured Service Provider. To configure the SAML component to correctly check this, the Issuer field in the SAMLRequestSettings property must be set to the Service Provider's EntityId.
Subject, InResponseTo, and Destination
When validating a SAML response and assertion, the InResponseTo attribute needs to be checked. For a SAML response, this is found in the SAMLResponse element, whereas in an assertion, it is found within the SubjectConfirmationData element. The InResponseTo attribute is used to check that the SAML response or assertion is "in response to" a SAML request made by the Service Provider. Before validating, the Id field in the SAMLRequestSettings property must be set to the Id of the matching request.
The SAMLResponse element has a Destination attribute and the assertion's SubjectConfirmationData element has the Recipient attribute. These two attributes check for the same information, ensuring that the SAML response and assertion were received by the intended Assertion Consumer Service endpoint. The SAML component checks this attribute by checking the ServiceProviderURIs collection to see if the matching URI has been added to the collection.
The assertion also checks the SubjectConfirmation element to ensure that the Method attribute is set to a valid method. The Web SSO profile defines that this method must be either bearer or sender-vouches, and any other method means the assertion should be discarded. This is automatically checked by the SAML component with no additional configuration needed.
AuthnStatement
The AuthnStatement element is unique to assertions. The only check done within this element is to ensure that the SessionNotOnOrAfter attribute has been passed if present in the AuthnStatement.
Status
The Status element is unique to the SAML response. When the Identity Provider is authenticating the user, it will set the Status element to the outcome of that process. Typically, this will be set to urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:status:Success if the user was able to successfully authenticate. If an issue occurs, then the Identity Provider will set it to a matching URI to inform the Service Provider why the user was unable to successfully authenticate. Any value that is not the success value is considered a failure when validating.
Access and Use an Assertion
Once the SAML response and the assertion have been parsed and validated by the SAML component, the user represented by the assertion can be considered authenticated. Assertions can contain more information than just proof that a user was authenticated by the Identity Provider. An assertion is typically broken up into three sections of information. The first is general information about the assertion. The other two are the AuthnStatment and AttributeStatement elements. As a note, an assertion can have multiple statements of the same type.
Generally, an assertion will contain information about a subject that represents the user as the subject of the assertion. Within a subject, the Identity Provider will define some type of name identifier. When we configured Microsoft Entra ID, we informed Microsoft that we would want this in the form of an email. After the SAML component parses the assertion, this name identifier can be found in the SubjectNameId field in the AssertionInfo property.
Other information generally found in the assertion includes some of the common conditions about assertions such as the ExpirationDate, NotBeforeDate, and OneTimeUse fields. These fields describe how and when the assertion should be trusted or discarded. Along with that, the Id field provides the assertion's identifier that is unique to this assertion.
AuthnStatement Element
Each AuthnStatement element provides information about the authentication event performed with the user. Information about when and how the user was authenticated along with session information are provided through these statements. If multiple statements are present, then the user has undergone multiple authentication events. These statements are parsed to the AssertionAuthnInfo collection.
The AuthnInstant field provides when the authentication event took place for the user. The ContextClassReference and ContextDeclaration fields provide information on how the user was authenticated. The SessionIndex and SessionExpiration fields describe the session that was established between the Service Provider (your application) and the subject (your user).
AttributeStatement Element
An AttributeStatement element is made up of one or more Attribute elements associated with the subject of the assertion. Each Attribute is a key-value pair representing a piece of information about a user. Sometimes the Attribute can have multiple values per key. For example, take the following Attribute about a user.
<Attribute Name="verified_emails">
<AttributeValue> email@test.com </AttributeValue>
<AttributeValue> other@example.com </AttributeValue>
</Attribute>
This Attribute is a list of emails that have been verified for the user. There are two ways to access these values using the SAML component. The first option is to use the AssertionAttributeInfo collection. This process requires that the application iterate through each AttributeStatement element in the collection, and then through each Attribute within that statement.
List<string> verified_emails = new List<string>();
for(int i = 0; i < saml.AssertionAttributeInfo.Count; i++){
if (saml.AssertionAttributeInfo[i].Name == "verified_emails" || saml.AssertionAttributeInfo[i].Name == "verified_email"){
for (int j = 0; j < saml.AssertionAttributeInfo[i].AttributeValueCount; j++) {
saml.AssertionAttributeInfo[i].AttributeValueIndex = j;
verified_emails.Add(saml.AssertionAttributeInfo[i].AttributeValueData);
}
}
}
The second option is to use the GetAssertionAttribute method. Although not as flexible, the method will search all the AttributeStatement elements in the assertion and return the first attribute with a matching name, if found. If the attribute has multiple values, that information will be listed in a semicolon-separated string.
string[] verified_emails = saml.GetAssertionAttribute("verified_emails").Split(';');
Build Service Provider Information
Sometimes, it is easier for your application to build its own metadata document that it provides to an Identity Provider. This is particularly useful for cases in which administrators need to set up multiple Identity Providers for the application. Microsoft Entra ID supports the parsing of metadata documents, allowing you to bypass much of the configuration process. The BuildServiceMetadata method can be used to create the metadata document that can be imported into Microsoft. The fields in the ServiceProviderMetadata property are used to configure the metadata document along with the ServiceProviderURIs and ServiceProviderSigningCert properties. The completed metadata document is found through the MetadataContent field within the ServiceProviderMetadata property.
SAMLDesktop Example
The SAMLDesktop component simplifies the SAMLWeb component further by hosting it's own web server and launching the browser for the user to use for your application. Since it is hosting it's own web server, it will also automatically retrieve, parse, and validate the SAML response as well. All of this is done with a single call to the AuthenticateUser methhod.
While most of the setup is the same, there are a few key differences. First, the ServiceProviderURIs collection is not included in the API. Instead, you setup the ACS URI using the WebServerBindings, WebServerPort, WebServerSSLCert, and WebServerSSLEnabled properties. Additionally, if using something like a relay server, the ReturnURL property can be set to specifiy a different location that will relay the SAML response to the embedded web server.
Additionally, there is no Single Logout Support since the specification recommends that Service Providers be actively listening for logout requests that are sent from the Identity Provider.
SAMLDesktop saml = new SAMLDesktop();
//Get Metadata
saml.RequestIdentityMetadata("https://login.microsoftonline.com/11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555/federationmetadata/2007-06/federationmetadata.xml?appid=66666666-7777-8888-9999-000000000000");
//Setup SAML Request
saml.SAMLRequestSettings.Binding = SAMLBindings.sbHTTPRedirect;
saml.SAMLRequestSettings.Issuer = "ServiceProviderId";
//Authenticate User using random web server port.
saml.AuthenticateUser();
We appreciate your feedback. If you have any questions, comments, or suggestions about this article please contact our support team at support@nsoftware.com.

