AMQPClassic Adapter for Microsoft BizTalk
Requirements: /n software Adapters for Microsoft BizTalk
Introduction
The /n software Adapters for Microsoft BizTalk include fully-managed .NET Adapters that seamlessly integrate with the BizTalk Messaging Pipeline. The /n software Adapters extend the features of BizTalk with advanced Internet communications and secure messaging capabilities.
There are many different BizTalk adapters currently supported: AS2 Adapters for EDI communications, FTPS, FTP, SFTP, SSH, Email adapters, etc. These adapters have completed the official adapter certification program (administered by Unisys) established by Microsoft for BizTalk server, which tests for scalability and interoperability with Microsoft BizTalk Server.
This guide will focus specifically on the AMQPClassic adapter, which adds AMQPClassic messaging capabilities to your BizTalk Server. If you're interested in using AMQPClassic communication in your BizTalk solution, you're in the right place. Before you continue reading, I recommend that you go ahead and download the product and follow along with me through the tutorial.
Contents
- Adapter Installation
- Adapter Properties - Send Port
- Usage - Send Port
- Adapter Properties - Receive Port
- Usage - Receive Port
Adapter Installation
Before installing you should stop the BizTalk host instance and close the BizTalk Administration Console. After you run the setup application, all of the necessary files will be installed on your system. The adapters will automatically be added to the BizTalk Administration Console, so we can begin using them in send ports and receive locations. If you open the BizTalk Administration Console and create a new receive location or send port, you'll see that the /n software AMQPClassic adapter is now available as a transport type.
Adapter Properties - Send Port
One common situation in which the AMQPClassic adapter might be used is one where files dropped in a local folder need to be sent as messages to an broker. In this situation, a receive location of transport type FILE would be configured in BizTalk to monitor a folder, and you would configure a Send port that will send the file payload picked up in this folder to the broker.
After you add a new Send Port and set the transport type to "nsoftware.AMQPClassic 2024" (also don't forget to set the Filters to associate this send port with the file pickup receive location), Clicking on the Configure button will bring up a new window called "nsoftware.AMQPClassic 2024 Transport Properties" where you will specify the details of how and where the AMQPClassic adapter should connect. There are eight groups of properties:
-
AMQPClassic
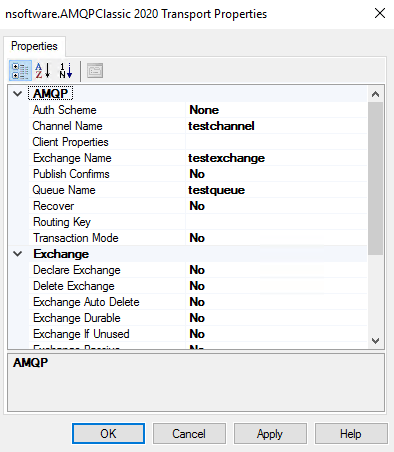
The first group of properties are AMQPClassic properties. These include some connection details as follows:
Auth Scheme The authentication scheme to use when connecting. Channel Name The name of the channel the message is associated with. Client Properties A collection of table fields that describe properties of the client. Exchange Name The name of the exchange. Publish Confirms Enables publish confirmations mode for a channel. Queue Name The name of the queue. Recover Requests the server to redeliver all messages on a given channel that have not been acknowledged. Routing Key The binding's routing key. Transaction Mode Whether the channel is operating in Transaction mode.
-
Exchange
The Exchange properties define settings for manipulating exchanges on the server:
Declare Exchange This is used to verify that an exchange named ExchangeName exists, and potentially creates it if no such exchange exists. Delete Exchange Specifies whether delete the exchange named ExchangeName. Exchange Auto Delete This specifies whether the server should automatically delete the exchange when all queues have been unbound from it. Exchange Durable This specifies what happens to the exchange in the event of a server restart. Exchange If Unused Specifies whether the server will delete the exchange if no queues are bound to it. Exchange Passive This specifies how the server will deal with a preexisting exchange. Exchange Type This specifies the exchange type.
- Logging
The Transport Log property is the only property here. If you click the + symbol next to the property this will expand the property and expose it's fields. You will see Location, Log Mode, and Log Type. By default the adapter will log only errors to the application event log. You can change the Log Mode to a mode with greater detail so that information event log entries are written to the event log during the course of execution. You may also change the Log Type so that events will be written to file instead of the event log. In that case you'll need to specify the full path to a file in the Location field.
-
Message
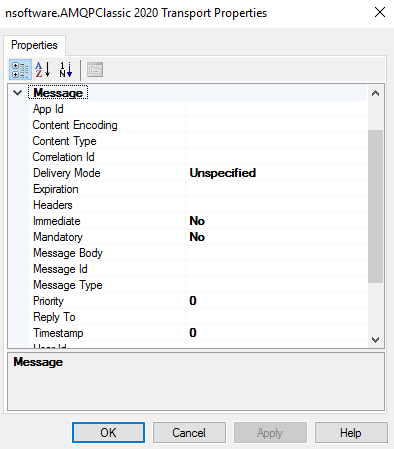
The Message properties specify details about the message to send. The following is a list of common properties used when downloading files. For complete details see the online help documentation.
Message Body This property specifies the contents to send in this message. If left unspecified the BizTalk message body will be used as the message content. The MessageValueType property should be used to specify the data type of the value. Message Type The message's type. Expiration The time-to-live value for this message. Delivery Mode The delivery mode of the message. -
Queue
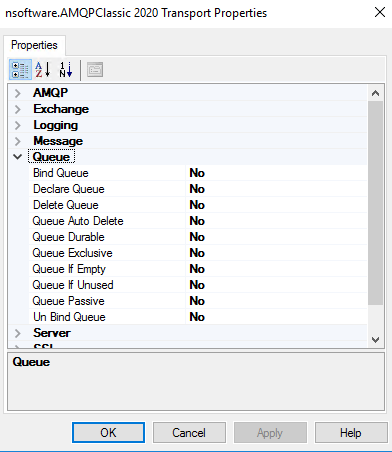
The Queue properties define settings for manipulating queues on the server:
Bind Queue This is used to verify that an exchange named ExchangeName exists, and potentially creates it if no such exchange exists. Declare Queue This is used to verify that a queue named QueueName exists; and potentially creates it if no such queue exists. Delete Queue Deletes the queue named QueueName. Queue Auto Delete This specifies whether the server should automatically delete the queue when all consumers have finished using it. Queue Durable This specifies what happens to the queue in the event of a server restart. Queue Exclusive Exclusive , if True , indicates that the queue may only be accessed by the current connection. Queue If Empty Specifies whether to delete the queue when consumers are attached. Queue If Unused Specifies whether to delete the queue when no messages are in it. Queue Passive This specifies how the server will deal with a preexisting queue. Un Bind Queue Unbind the queue to the exchange with given RoutingKey. -
Server Properties
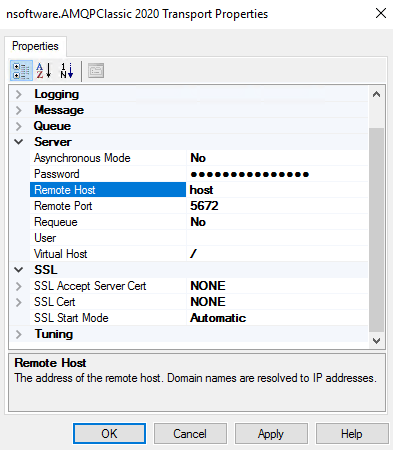
The Server properties allow you to specify the login credentials and remote host information.
Asynchronous Mode Indicates whether the server handles the request in asynchronous mode. Password The user's password. Remote Host The address of the remote host. Domain names are resolved to IP addresses. Remote Port The port of the AQMP server (default is 5672). Requeue This property controls how the server should attempt to redeliver the messages awaiting acknowledgement. Session Name The name of the session. User A username to use for SASL authentication. Virtual Host The virtual host to connect to. -
SSL Properties
The SSL Properties govern whether or not a server's certificate is accepted, whether SSL client (certificate based) authentication is performed, and what type of SSL is performed.
SSL Accept Server Cert Instructs the adapter to accept the server certificate which matches the one specified if it is not already trusted by the system. For testing you can expand this property and set the Accept Any field to Yes. This tells the adapter to always accept the server's certificate. SSL Cert If set to a valid certificate the adapter will attempt SSL client (certificate based) authentication. Typically this is not required. SSL Start Mode Determines what type SSL is performed. This can be set to automatic, explicit, implicit, or none. With a value of automatic the adapter will use the value of Remote Port to determine what type of SSL to perform. -
Tuning Properties
Firewall This may be expanded to configure the firewall type, host, port, user, and password if needed. Other This allows you to specify additional configuration settings in the format configname1=value1. See the Configuration section of the documentation for a list of supported settings.
Usage - Send Port
In order to configure a send port to send message data from the pick-up folder to an AMQPClassic broker, I only need to set a few of these properties:
- There are three required properties that must be set in the Server properties. "Remote Host" and "Remote Port" should be set to the AMQPClassic broker you wish to connect to. Additionally, "Channel Name" must be set.
- To declare an exhange on the server, set "Declare Exchange" to "Yes" and specify any other Exchange properties as needed.
- To declare a queue on the server, set "Declare Queue" to "Yes" and specify an other Queue properties as needed. Queues can also be bound to an exchange by setting "Bind Queue" to "Yes".
- By default the message will be published to the server's default (no-name) exchange and the "Queue Name should be set to use as the routing key. To publish to a specific exchange, the "Exchange Name" should be set as well as the "Routing Key".
- The message properties including a "hard-coded" "Message Body" may be set. Otherwise the contents of a file in a receive location will be sent as the message content. See the documentation for more details on these properties.
To test, I'll set the Filter of the send port to BTS.InboundTransportLocation == "C:\test\in\*.*", the location of my File adapter receive location. Then I'll enable the ports, start BizTalk Server and drop some test files. The adapter will transfer the picked up file content to the AMQPClassic broker.
Adapter Properties - Receive Port
Another common situation in which the AMQPClassic adapter might be used is one where messages on an AMQP broker need to be retrieved in a BizTalk orchestration or passthrough configuration so that these messages can be used locally or automatically transferred elsewhere. In this situation, a receive location of transport type AMQPClassic would be configured in BizTalk to monitor this.
After you add a new Receive Location and set the transport type to "nsoftware.AMQPClassic 2024" (also don't forget to set the Filters to associate this receive location with the file send port), Clicking on the Configure button will bring up a new window called "nsoftware.AMQPClassic 2024 Transport Properties" where you will specify the details of how and where the AMQPClassic adapter should connect. Many of these properties are the same as those documented above in the Send Port section. Here I will only document the properties specific to using the adapter in a receive location, since many of the properties have the same meaning as in the above description of the AMQPClassic adapter in a send port.
- AMQP, Exchange, Logging, Queue, Server,and SSL Properties
The adapter has the same AMQP, Exchange, Logging, Queue, Server,and SSL properties in a receive location as in a send port.
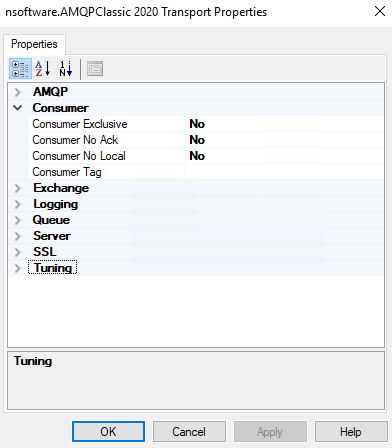
- Consumer Properties
Consumer Exclusive The ConsumerExclusive property, if True, will cause the adapter to request that the server create an exclusive consumer. Attaching an exclusive consumer to a queue prevents any other consumers from consuming messages from that queue. Consumer No Ack The ConsumerNoAck property controls whether the server will expect the adapter to acknowledge each message delivered. Consumer No Local The ConsumerNoLocal property, if True, ensures that the consumer never consumes messages published on the same channel. (Note that this functionality is not available on RabbitMQ servers, which ignore the NoLocal parameter). Consumer Tag ConsumerTag is a string which uniquely identifies the new consumer on the specified channel. If empty string is passed for ConsumerTag, the server will generate a consumer tag automatically when it creates the consumer.
Usage - Receive Port
In order to configure a receive port to receive messages from the remote AMQPClassic server, again I only need to set a few of these properties:
- For the Server properties, I'll use the same settings as in the above send port example since I am connecting to the same server.
- I must also set "Channel Name" and "Queue Name" to specify the channel and queue to consume messages from.
- The Consumer properties may also be set as needed. Other Exchange and/or Queue properties may be set, but these are not necessary.
To test, I will create a send port of transport type FILE with a filter pointing to this new AMQPClassic receive location. Then I will enable the ports, start BizTalk Server and publish a message to the AMQPClassic broker. On the next polling interval the adapter will connect to the AMQPClassic broker, receive the message, and pass to the BizTalk Message Box for consumption by the FILE send port. The response received by the adapter will be used as the body of the submitted BizTalk message.
Conclusions
This article demonstrates the ease of use of the AMQPClassic adapter in particular, but /n software provides a full set of adapters for connecting to various types of internet servers. The adapter properties are kept to a minimum for simplicity, but we make an effort to provide those properties that are necessary for effective control over configurations.
We appreciate your feedback. If you have any questions, comments, or suggestions about this article please contact our support team at support@nsoftware.com.

